Wonderful Info About How To Check For Asterixis

This video introduces you to asterixis and its most common causes.check us out on facebook for daily free review questions and updates!
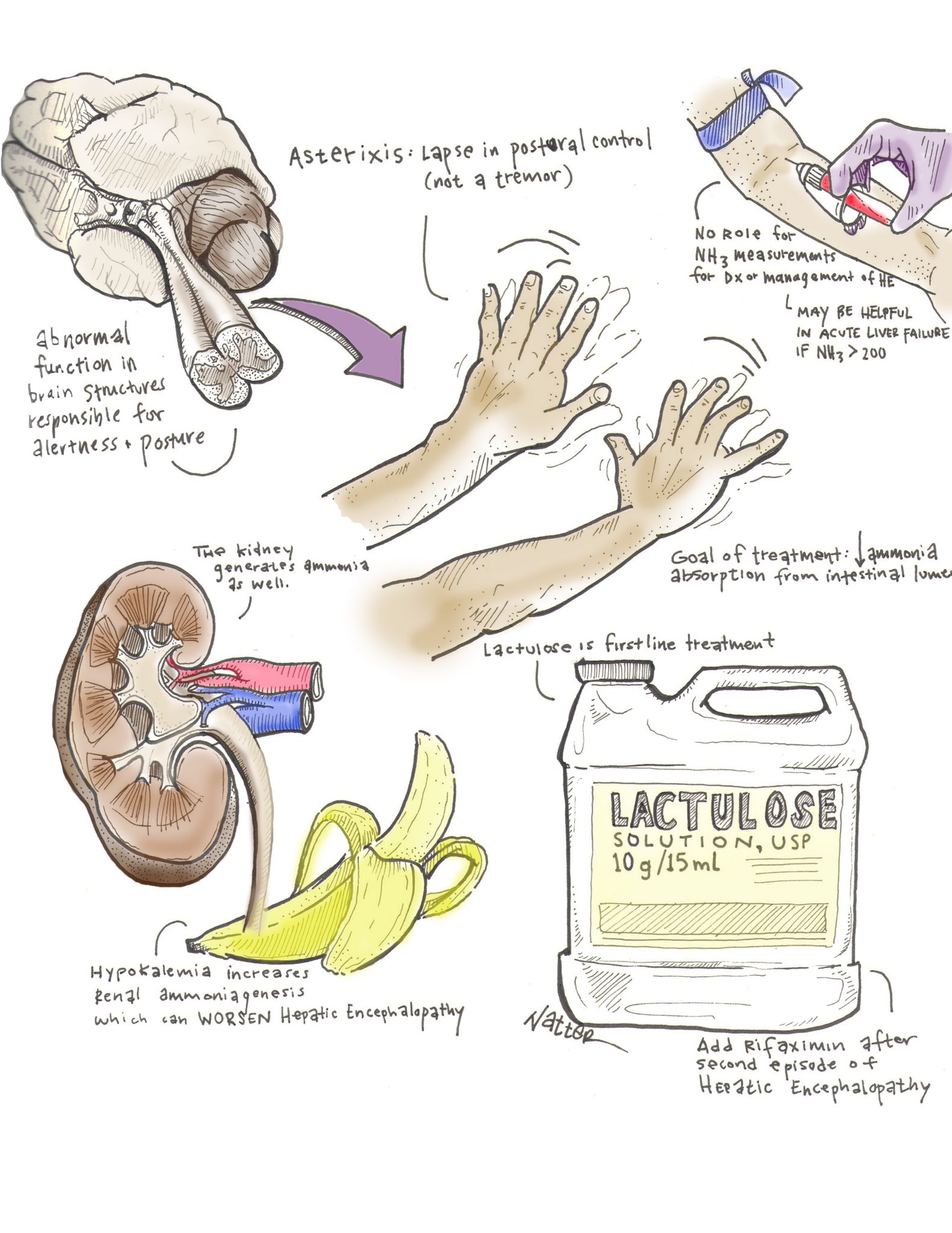
How to check for asterixis. Blood tests may also reveal symptoms such as high calcium, low. These may include a ct scan, blood test, liver enzymes test, albumin level, serum creatinine, and urine test. A person with asterixis will flap their wrists involuntarily when told to flex their wrists and spread their fingers.
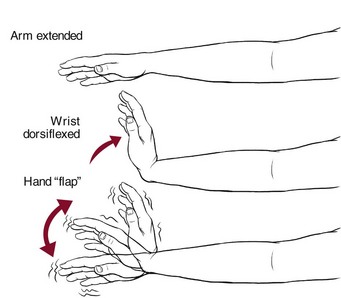
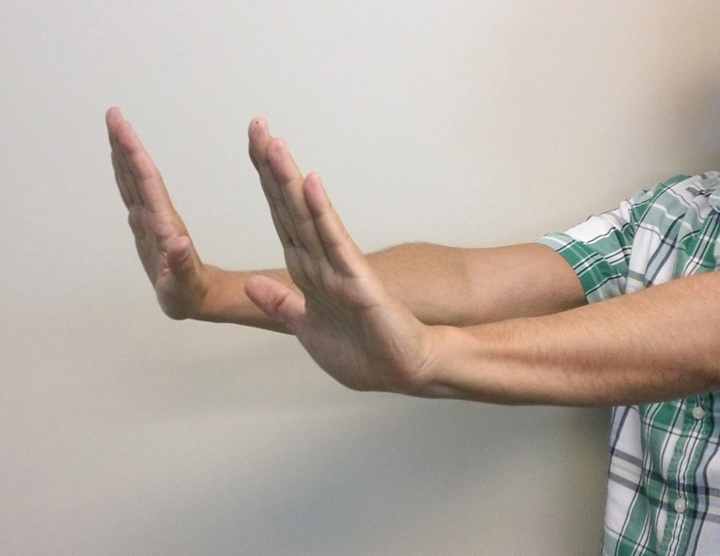
Look for an intermittent loss of tone in the wrists, with the appearance of a flap. Asterixis can be elicited on physical examination by having the patient extend their arms, dorsiflex the wrists, and spreading the fingers (similar to pushing against a wall) with. Asterixis, also known as hepatic flap or uraemic flap, is an important sign of metabolic encephalopathy that occurs due to dysregulation of the diencephalic motor centers in the brain.
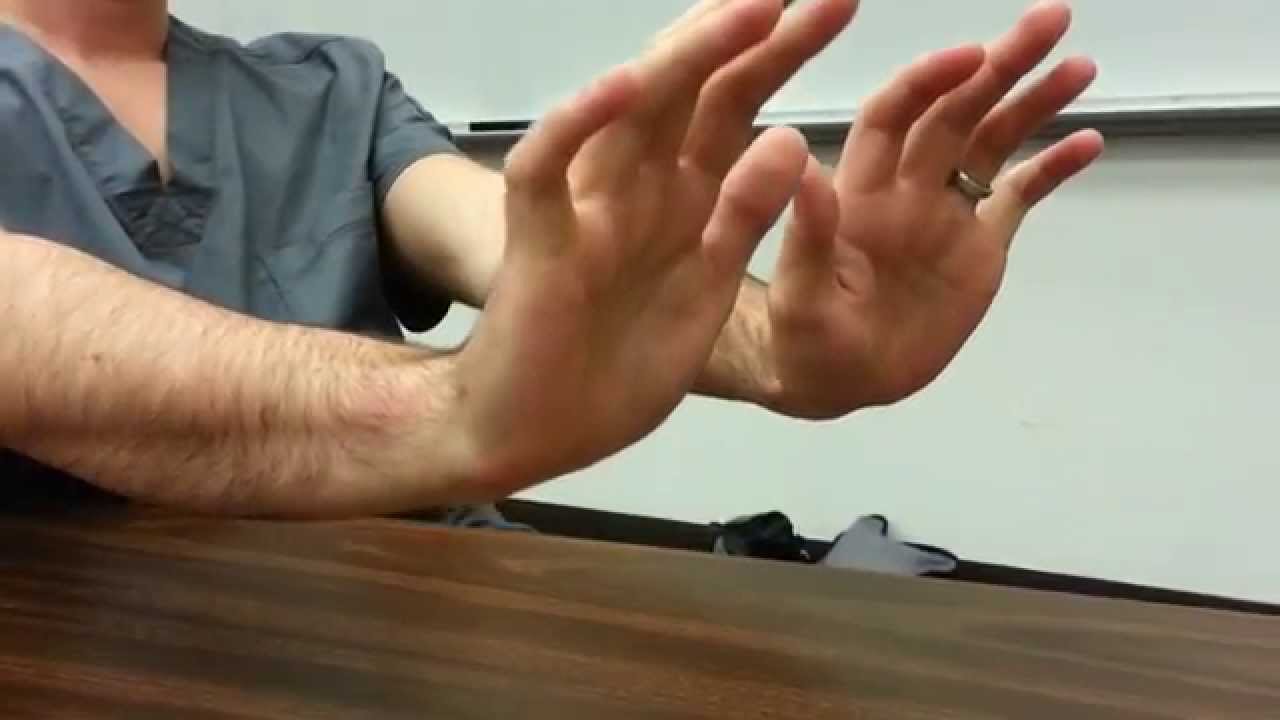
Diagnosing asterixis the process of diagnosing this condition is like most diagnoses and examinations. Asterixis is tested by something called a hand flap neuro test, which involves the patient stretching their arms straight out in front of them and then pulling their wrists backward. This motor disorder is myoclonus.
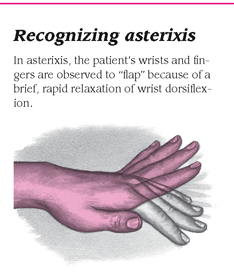
Asterixis is the inability to maintain posture due to a metabolic encephalopathy. Since asterixis is a disorder of posture, it makes sense that in eliciting the sign the clinician should ask the patient to adopt a constant posture that is then held against gravity. Asterixis may occur in individuals with toxic metabolic encephalopathy as a result of hepatic, renal or pulmonary disorders.
Asterixis, also known as hepatic flap or uraemic flap, is an important sign of metabolic encephalopathy that occurs due to dysregulation of the diencephalic motor centers in the brain. The doctor will ask to discuss your medical history, making note. [ 1, 9] testing asterixis at the hip joint involves.
Patient is in altered sensorium admitted in critical care unit and has rigidity truncal more than peripheral, this is the method to check myoclonus in a unco. This can be elicited on physical exam by having the patient extend their arms and bend their hands back. Ask the patient to place their arms up and out in front of them with the wrists extended.
Asterixis can be elicited on physical examination by having the patient extend their arms, dorsiflex the wrists, and spreading the fingers (similar to pushing



![2015] Hepatic Encephalopathy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015hepaticencephalopathy-151117004212-lva1-app6891/85/2015-hepatic-encephalopathy-33-320.jpg?cb=1447721069)